How Do Contrast Sensors Work?
Contrast sensors are photoelectronic sensors that work according to the principle of a reflex sensor: Emitted light is reflected by the object, reabsorbed and evaluated. Contrast sensors are used to detect markings based on differences in contrast. They are characterized by high switching speeds and low jitter. Different contrast detection technologies are available to achieve the best possible detection:
- Laser red light + monochrome photodiode
- White light + monochrome photodiode
- White light + RGB photodiode
What Is the Difference Between Light and Laser Light?
Light consists of electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye that propagates in different wavelength ranges when emitted by a light source. Laser light is created by stimulated emission that amplifies light, i.e. high concentrations of rectified light waves are bundled into a beam.
What Is a Color Space and Which Is Particularly Relevant for Sensors?
A color space is a defined color coordinate system used to systematize and standardize colors. This determines the amount of colors and the method of color representation. In a color space, colors are described by coordinates where the axes represent different color properties, such as color intensity, brightness, tone or saturation. The RGB and CMYK color spaces are particularly relevant for industry. The RGB color space is used for sensors, because they collect color information in the form of red, green and blue color channels.
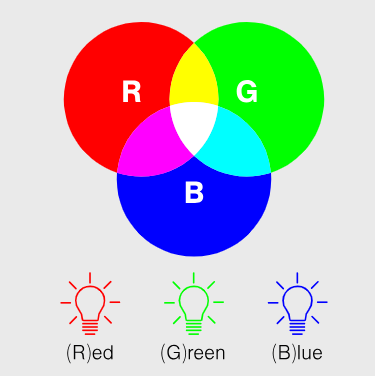
RGB uses light to create colors by combining red, green and blue.
The CMYK color space is mainly used in printing and produces colors with cyan, magenta, yellow and black.
What Is White Light Based on the RGB Color Space?
The RBG color model works as an additive color mix. White light is created by mixing red, green and blue light. Black results in the absence of light of any wavelength.
Contrast Sensor Technologies
How Do Contrast Sensors with White Light Work?
Contrast sensors with white light LED emit white light in the form of a rectangular light spot that is reflected back from the surface to the receiver of the sensor, which then evaluates this light.

Receiver with RGB Photodiode (P1PWxxx):
The receiver consists of three areas corresponding to the RGB color space. Depending on the color of the contrast marking, the light is reflected back to the receiver according to the reflection properties and evaluated based on the three channels.

Receiver with Monochrome Photodiode (WM03xxx):
The photodiode of the receiver consists of a single continuous surface. Depending on the color of the contrast marking, the light is reflected back to the receiver according to the reflection properties. The receiver evaluates the received brightness and sorts it into a grayscale.
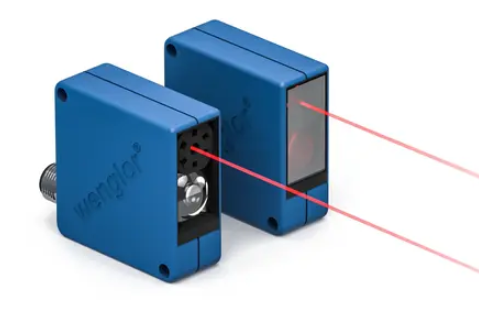 How Do Contrast Sensors with Laser Light Work?
How Do Contrast Sensors with Laser Light Work?
Contrast sensors with laser light emit a spot of red laser light, the reflection of which is evaluated by the receiver. The receiver uses a monochrome photodiode. Contrast sensors with laser light are available in a digital and an analog version:
- Digital version (YM24PAH, YP11VAH): The switching threshold is set to a certain brightness level. This brightness value is then compared with the amount of light reflected by the object.
- Analog version (YP11MGV): The analog output outputs a voltage proportional to the brightness. The output voltage increases along with the degree of brightness.
Contrast Sensor Applications:

Color Check of Objects:
To ensure high product quality, the visual characteristics must also be monitored and controlled at all times in the production process. Contrast sensors can detect color differences, enabling quality control based on visual appearance characteristics. For example, the color of bottle caps is checked to ensure that the correct caps are always used in a container.
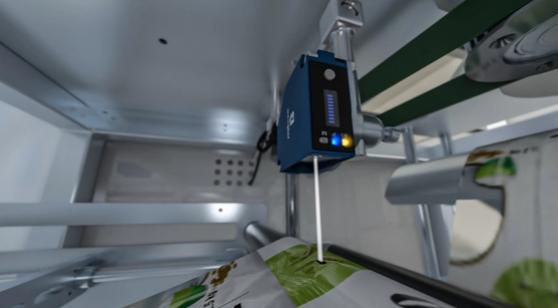
Print Mark Recognition:
Print marks are colored markings or gray blocks in various percentages printed on packaging materials. They can be recognized photoelectronically and then trigger control commands on a connected processing machine. Print marks are used to control various processes:
- Alignment and positions of objects
- Cutting, welding, and bonding processes
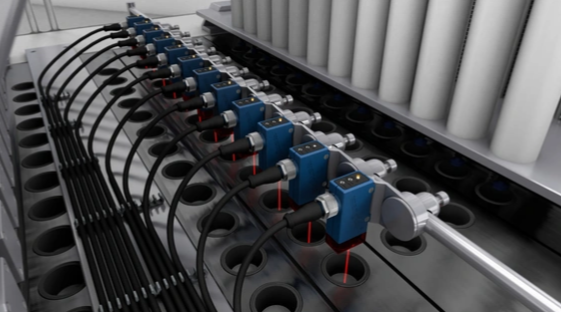
Detection of Contrast Differences:
Contrast differences are different brightness levels of objects. Brightness levels are compared with reference values to solve various applications:
- Differentiation of objects based on contrast values
- Presence check of inserts in an assembly process
- Presence check of very flat objects against a background
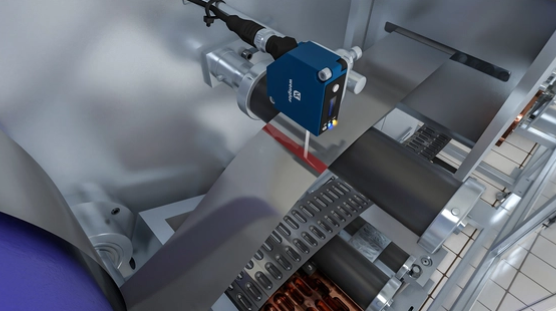
Checking the Material End with Visual Marks:
Film material is processed on rolls in production technology. During production, the material is unwound from the roll. Marking stripes are applied to mark the end of the roll. These are detected by contrast sensors to ensure that a roll change is initiated in good time.
Industries for Preferred Use of White Light LED Contrast Sensors:
- Packaging
- Food
- Printing
Industries for Preferred Use of Contrast Sensors with Laser Light:
- Automotive
- Plastics
How Does Teaching in the Contrast Sensors to the Application Work?
Contrast sensors with laser light are adjusted using a potentiometer. This means that the threshold value is set manually.
Contrast sensors with white light LED are taught in at the touch of a button by the sensor automatically calculating the switching threshold via the teach-in key. Three different teach-in modes are available for this:
- Two-point teach-in: With two-point teach-in, the object, i.e. the mark, is taught in during one teach-in process and the background in another teach-in process. Using both measured values acquired and saved in this way, the sensor calculates the switching point so that it lies between the two teach-in points.
- Dynamic teach-in: With dynamic teach-in, the sensor is switched to recording mode operation, allowing for automatic teach-in. Measured values are recorded in this mode. After the recording mode has been exited, a switching point is calculated between the minimum and maximum measured values.
Outputs and Interfaces:
Digital Switching Output:

Contrast values can be taught in via a digital switching output via teach-in or potentiometer. If the taught-in contrast value is reached, the sensor outputs a switching signal at the output, whereby contrast or print marks are detected, for example.
Analog Output:

The contrast value is output as a linearly proportional current (4…20 mA) or voltage value (0…10 V) via an analog output. This allows the brightness curves to be monitored precisely.
IO-Link:
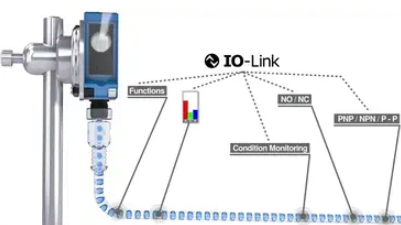
IO-Link technology enables standardized communication with sensors and actuators around the world. This is point-to-point communication.
Mounting Instructions for Contrast Sensors:


